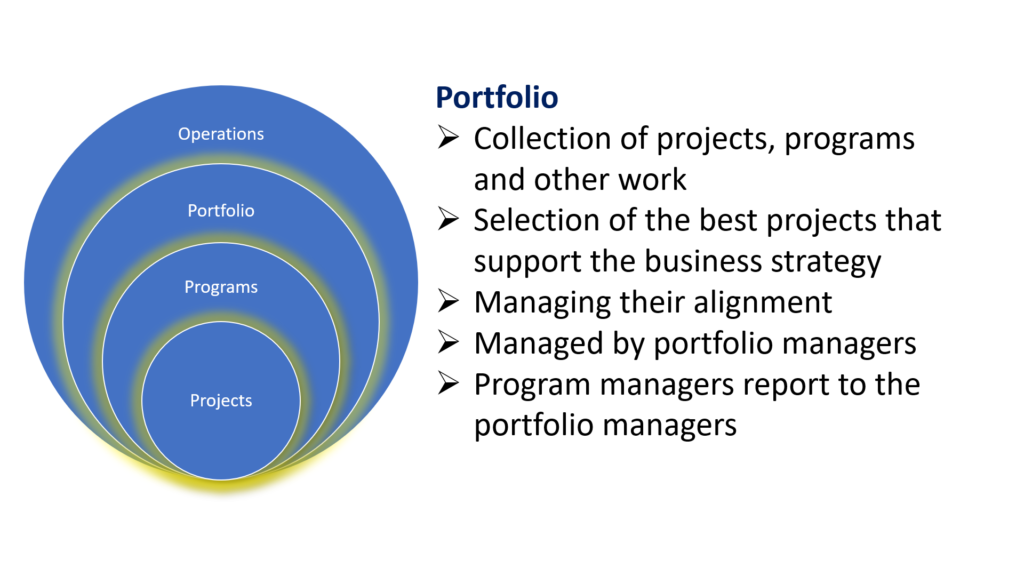
Organizations have business goals to accomplish
- For this they develop business strategies
- Business strategies are implemented through projects and programs
- Portfolio management involve;
- Selecting the right projects / programs which are in true alignment to the organizations strategy for growth
- Maintaining this alignment throughout
- Portfolios are managed by portfolio managers
- Portfolios can include projects, programs and other work
Detailed explanation
Portfolio management is the systematic process of strategically selecting and managing a collection of programs, projects, or investments to achieve an organization’s overall objectives and maximize value. It involves making decisions about which programs or projects to undertake, allocating resources appropriately, and monitoring performance to ensure alignment with strategic goals.
Here are the key components of portfolio management:
- Strategic Alignment: Portfolio management begins with aligning the portfolio with the organization’s strategic objectives and goals. This involves understanding the organization’s mission, vision, and priorities, and selecting programs and projects that contribute to achieving them.
- Selection and Prioritization: Portfolio managers evaluate potential programs and projects based on factors such as their alignment with strategic objectives, potential benefits, resource requirements, risks, and constraints. They prioritize initiatives according to their importance and potential impact on the organization.
- Resource Allocation: Portfolio management involves allocating resources, including financial resources, personnel, and other assets, to programs and projects in a way that maximizes value and minimizes risk. This may involve balancing competing priorities and optimizing resource utilization across the portfolio.
- Performance Monitoring and Reporting: Portfolio managers monitor the performance of programs and projects within the portfolio to ensure they are progressing according to plan and delivering the expected benefits. They track key performance indicators (KPIs), assess risks, and make adjustments as needed to keep the portfolio on track.
- Risk Management: Portfolio management includes identifying, assessing, and managing risks at the portfolio level. This may involve diversifying the portfolio to reduce overall risk, implementing risk mitigation strategies, and monitoring risk exposure over time.
- Decision Making: Portfolio managers make strategic decisions about which programs and projects to initiate, continue, modify, or terminate based on their alignment with strategic objectives, performance, resource availability, and other factors. These decisions are often made in collaboration with senior leadership and stakeholders.
- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Portfolio management involves communicating with stakeholders, including executives, sponsors, project managers, and team members, to ensure alignment, manage expectations, and address concerns. Effective stakeholder engagement is essential for gaining support and buy-in for portfolio decisions.
The linkages between portfolio, programs, projects, and operations are essential for aligning organizational activities with strategic objectives and maximizing overall effectiveness. Here’s how these components are interconnected:
- Portfolio and Programs:
- Portfolios consist of a collection of programs, projects, and operational activities that collectively contribute to achieving strategic objectives.
- Programs within a portfolio are typically grouped together based on their alignment with common strategic goals or business objectives.
- Portfolio management involves selecting and prioritizing programs to include in the portfolio, ensuring they collectively support the organization’s strategic direction.
- Portfolio and Projects:
- Projects are individual endeavors aimed at creating a unique product, service, or result.
- Projects selected for inclusion in a portfolio are chosen based on their strategic importance and potential to deliver value to the organization.
- Portfolio management involves evaluating and prioritizing projects to ensure they align with the portfolio’s strategic objectives and contribute to overall success.
- Portfolio and Operations:
- Operations represent the ongoing, day-to-day activities that sustain an organization’s business functions.
- Operations provide the foundation and support for both projects and programs within a portfolio.
- Portfolio management considers the impact of portfolio decisions on ongoing operations and ensures that resources are allocated effectively to support both strategic initiatives and routine business activities.
- Programs and Projects:
- Programs are collections of related projects managed together to achieve common strategic objectives.
- Projects are individual endeavors within programs that contribute to the program’s overall goals.
- Programs provide the framework for coordinating and integrating multiple projects, ensuring that they work together synergistically to achieve desired outcomes.
- Programs and Operations:
- Operations provide the resources and support necessary for executing programs and their constituent projects.
- Programs may rely on ongoing operational activities to provide funding, personnel, infrastructure, and other resources needed for successful implementation.
- Operations may also benefit from improvements or changes resulting from program initiatives, leading to increased efficiency or effectiveness in day-to-day operations.
- Projects and Operations:
- Projects often result in deliverables or changes that impact ongoing operations.
- Operations provide the resources and environment in which projects are executed, including personnel, facilities, equipment, and infrastructure.
- Effective coordination between projects and operations is essential to ensure smooth project execution and the successful integration of project outcomes into routine business activities.
In summary, the linkages between portfolio, programs, projects, and operations are critical for aligning organizational activities, optimizing resource allocation, and achieving strategic objectives. Effective management of these linkages ensures that initiatives are prioritized, coordinated, and executed in a way that maximizes overall value and contributes to organizational success.
Roles and responsibilities of portfolio managers
Portfolio managers play a crucial role in overseeing and managing the collection of programs, projects, and operational activities that make up an organization’s portfolio. Their responsibilities typically include strategic planning, decision-making, resource allocation, risk management, and stakeholder engagement. Here’s a breakdown of the key roles and responsibilities of portfolio managers:
- Strategic Planning:
- Align the portfolio with the organization’s strategic objectives and goals.
- Identify and prioritize programs and projects that support strategic priorities.
- Develop long-term portfolio strategies and roadmaps.
- Portfolio Selection and Prioritization:
- Evaluate potential programs and projects based on their alignment with strategic objectives, potential benefits, risks, and resource requirements.
- Prioritize initiatives according to their importance and potential impact on the organization.
- Make decisions about which programs and projects to include in the portfolio.
- Resource Allocation:
- Allocate resources, including financial resources, personnel, and other assets, to programs and projects in a way that maximizes value and minimizes risk.
- Optimize resource utilization across the portfolio and balance competing priorities.
- Monitor resource availability and make adjustments as needed.
- Performance Monitoring and Reporting:
- Monitor the performance of programs and projects within the portfolio to ensure they are progressing according to plan and delivering the expected benefits.
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to assess portfolio performance.
- Provide regular reports and updates to stakeholders on portfolio status, progress, and risks.
- Risk Management:
- Identify, assess, and manage risks at the portfolio level.
- Develop risk management strategies and contingency plans to address potential threats to portfolio success.
- Monitor risk exposure and take proactive measures to mitigate risks as needed.
- Decision Making:
- Make strategic decisions about which programs and projects to initiate, continue, modify, or terminate based on their alignment with strategic objectives, performance, resource availability, and other factors.
- Collaborate with senior leadership and stakeholders to make informed decisions about portfolio priorities and resource allocation.
- Stakeholder Engagement:
- Communicate with stakeholders, including executives, sponsors, project managers, and team members, to ensure alignment, manage expectations, and address concerns.
- Engage stakeholders in portfolio planning, decision-making, and governance processes.
- Build and maintain strong relationships with key stakeholders to foster support for portfolio initiatives.
- Governance and Oversight:
- Establish and maintain a governance structure for the portfolio, including roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes.
- Provide oversight and guidance to program and project managers to ensure alignment with portfolio objectives and priorities.
- Ensure compliance with organizational policies, standards, and best practices.
In summary, portfolio managers play a critical role in driving organizational success by aligning portfolio activities with strategic objectives, optimizing resource allocation, managing risks, and engaging stakeholders effectively. Their responsibilities encompass strategic planning, decision-making, resource management, performance monitoring, risk management, stakeholder engagement, and governance.

