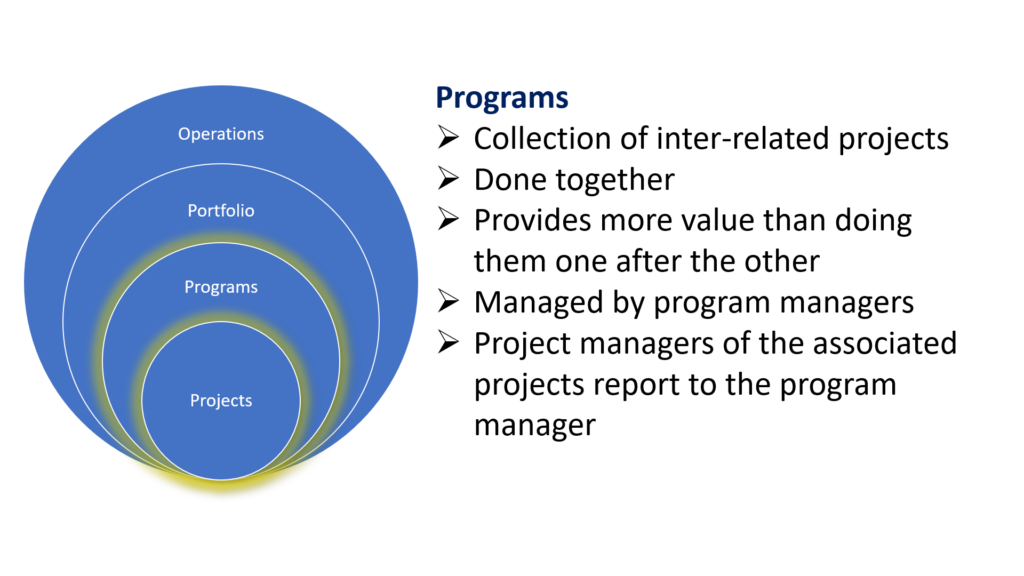
- Collection of inter-related projects
- When these inter-related projects are executed together produce better results
- Programs are managed by Program managers
- The individual projects which are part of the program are managed by Project managers
- The project managers of the individual projects that constitute a program, reports to the program manager
Here are some key aspects of programs:
- Strategic Alignment: Programs are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives and goals. They are designed to deliver benefits that support the overarching mission and vision of the organization.
- Complexity and Interdependence: Programs typically involve multiple projects that are interdependent and complex. These projects may share resources, dependencies, and deliverables, requiring coordinated management and oversight.
- Long-term Focus: Programs often have a longer timeframe than individual projects and may span months or even years. They involve ongoing planning, monitoring, and adjustment to ensure alignment with strategic priorities.
- Benefits Management: Programs focus on delivering benefits to the organization, which may include increased efficiency, cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, or competitive advantage. Benefits management is a key aspect of program governance.
- Governance Structure: Programs have a governance structure that provides oversight, decision-making authority, and accountability. This structure may include program managers, steering committees, and stakeholders responsible for guiding and monitoring program activities.

