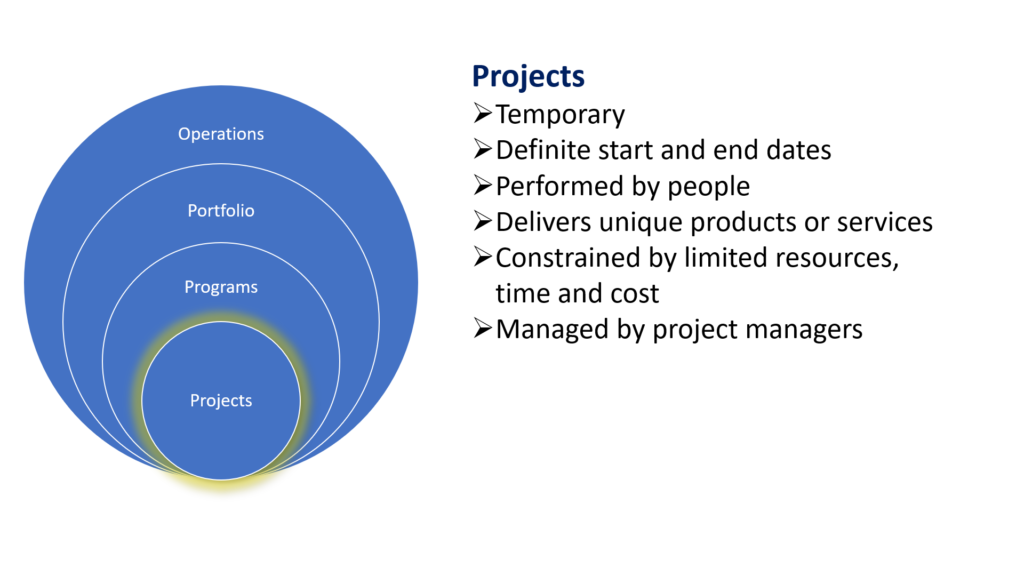
Key characteristics of projects;
- Temporary endeavour
- Have specific start and end dates
- Delivers unique products or services as output
- Performed by people
- Limited by the triple constraints of scope, cost and time
- A project is considered as successful, if it is completed within agreed upon time, cost and met the scope
- The success criteria of the project is also linked to the achievement of the business case of the project as well
- Projects are managed by Project managers in predictive or traditional project management. In agile or adaptive project management that role is performed by the Iteration manager or Scrum Master if the framework used is Scrum
Here are examples of projects:
- Construction Project: Building a new office complex.
- Objective: Construct a modern office space to accommodate 500 employees.
- Scope: Design, permits, site preparation, construction, and interior finishing.
- Timeline: 18 months.
- Resources: Architects, engineers, construction workers, materials, machinery.
- Success Criteria: Completed within budget, on time, meeting quality standards, and satisfying safety regulations.
- Software Development Project: Creating a mobile application.
- Objective: Develop an app for online food delivery.
- Scope: Requirement gathering, design, development, testing, deployment.
- Timeline: 6 months.
- Resources: Developers, designers, testers, servers, software tools.
- Success Criteria: App launched with all planned features, user-friendly interface, minimal bugs, positive user feedback, meeting performance metrics.
- Marketing Campaign Project: Launching a new product.
- Objective: Introduce a new line of organic skincare products.
- Scope: Market research, branding, advertising, packaging design, product launch event.
- Timeline: 3 months.
- Resources: Marketers, designers, copywriters, event planners.
- Success Criteria: Increased brand visibility, positive customer perception, high sales volume, media coverage, and reaching target demographics.

